Ultrasonographic Manifestations of Primary Hepatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case Report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3941/jrcr.5737Abstract
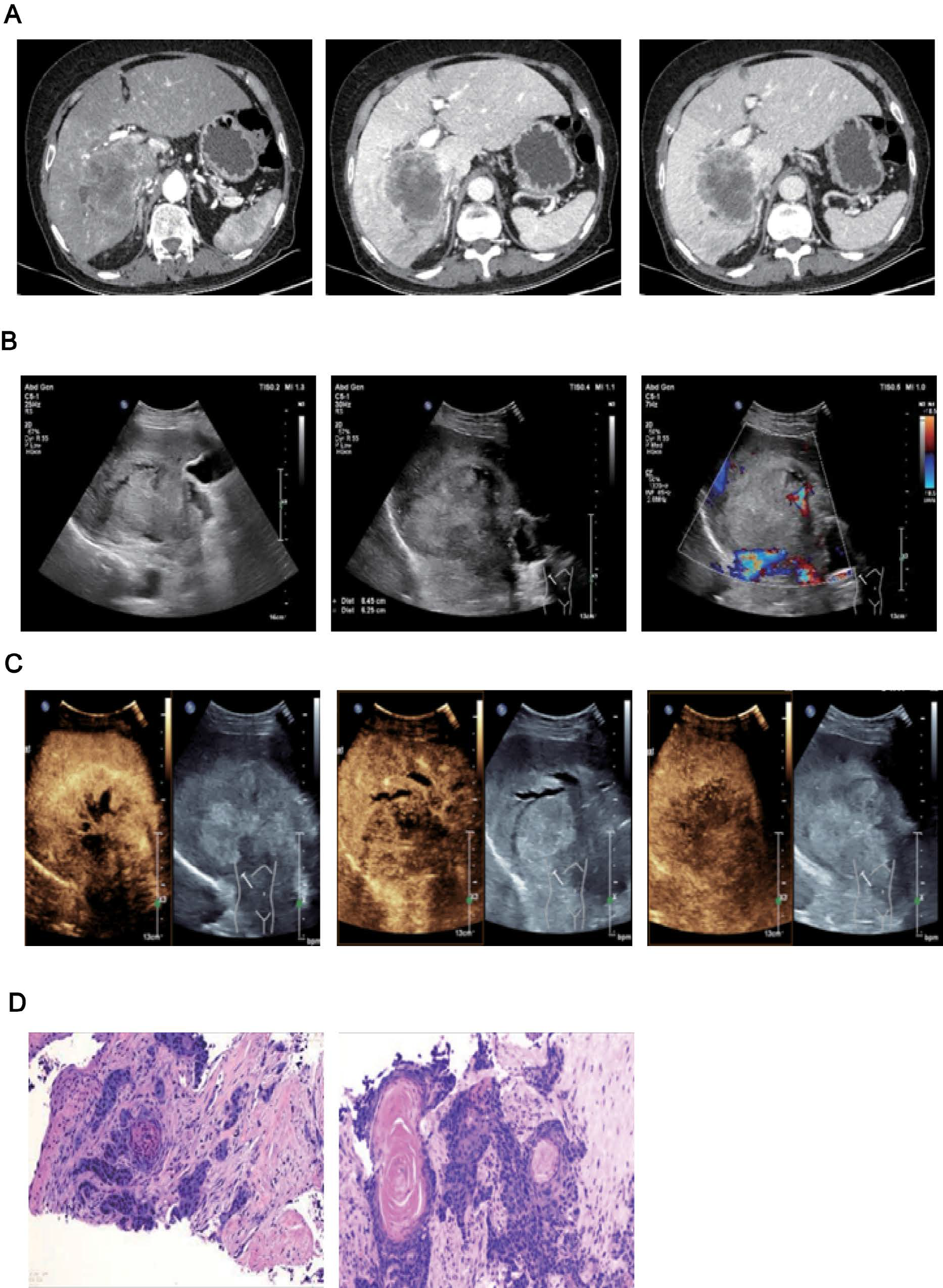
Primary squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the liver is a rare type of cancer. Most patients are elderly men. This disease is difficult to diagnose, highly invasive, has a poor prognosis, and there are extremely few reports in domestic and foreign literatures, which are basically mainly case reports. This article reports a patient with primary squamous cell carcinoma of the liver and conducts a relevant literature review to improve clinicians' diagnosis of primary squamous cell carcinoma of the liver. In July 2024, our hospital admitted a 58-year-old female patient. Abdominal CT tomography considered cholangiocarcinoma of the liver; contrast-enhanced liver ultrasound suggested a malignant enhancement pattern, with a greater possibility of hepatocellular carcinoma. Later, after a puncture biopsy of the space-occupying lesion in the liver under ultrasound guidance, the analysis of the biopsy sample indicated squamous cell carcinoma. Therefore, the doctors in our hospital carried out imaging examinations to find the primary lesion. The results showed that the space-occupying lesion was primary squamous cell carcinoma of the liver, accompanied by metastasis to the hilar and abdominal lymph nodes. The patient was treated with Sintilimab + Bevacizumab and was discharged from the hospital after the condition stabilized.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Radiology Case Reports

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The publisher holds the copyright to the published articles and contents. However, the articles in this journal are open-access articles distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 License, which permits reproduction and distribution, provided the original work is properly cited. The publisher and author have the right to use the text, images and other multimedia contents from the submitted work for further usage in affiliated programs. Commercial use and derivative works are not permitted, unless explicitly allowed by the publisher.





