Pancreatic Transplant Jejunitis Complication: A Case Report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3941/jrcr.%205644Abstract
Background
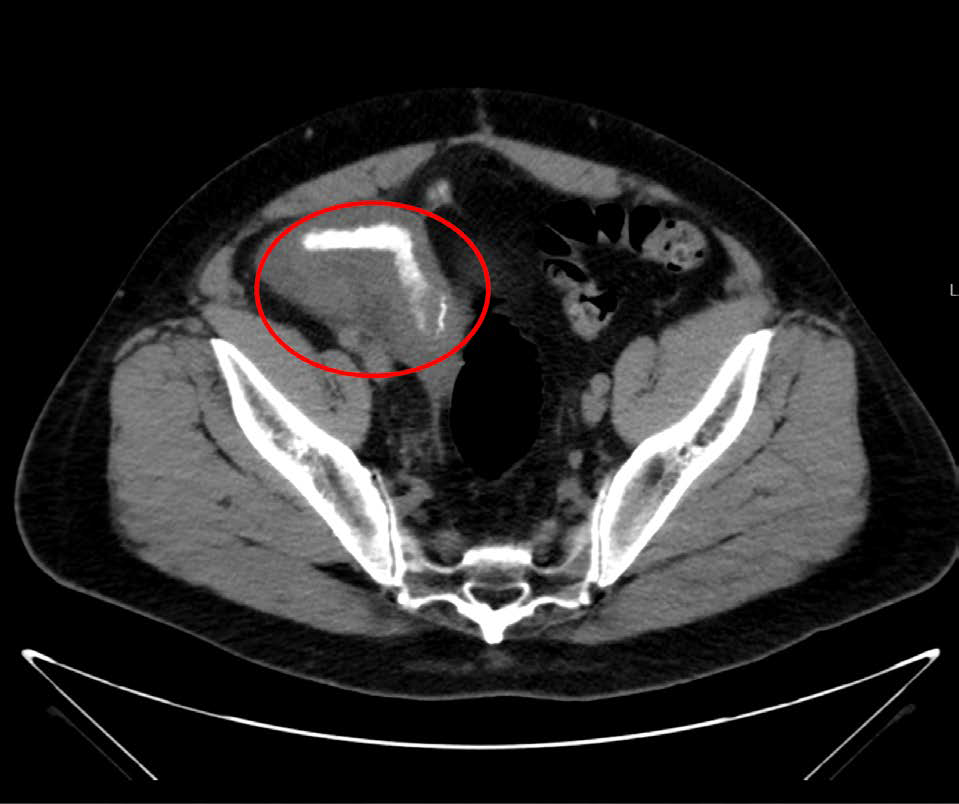
Pancreas transplantation aims to achieve stable glycemic control, often leading to insulin independence, while improving quality of life and reducing secondary complications associated with diabetes. One of the most common surgical approaches to the transplant is with a segment of the donor duodenum followed by a side-to-side duodenojejunal anastomosis. Complications of the procedure exist and it is important to conduct a follow-up CT scan post-transplant, especially if the patient complains of abdominal pain. Jejunitis should be considered in the differentials and a CT scan can help aid in confirmatory diagnosis.
Case presentation
Patient X, a 36-year-old male, recently underwent a pancreas transplant. Postoperatively, he presented with abdominal pain, leading to a workup with CT imaging that revealed jejunitis (inflammation of the jejunum), a condition that may be related to his recent transplant surgery.
Conclusion
Jejunitis is a complication of pancreatic transplant that can be identified with a follow-up CT scan. It is imperative to conduct a follow-up CT scan in a pancreatic transplant patient with any abdominal complaints to rule out infection, inflammation, or bleeding. Jejunitis should be added to the list of possible differential diagnosis as its symptoms may mimic other post-transplant complications.
Keywords: Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 (DM Type 1), Pancreatitis, Transplant, Jejunum, computed tomography (CT) scan
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Radiology Case Reports

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The publisher holds the copyright to the published articles and contents. However, the articles in this journal are open-access articles distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 License, which permits reproduction and distribution, provided the original work is properly cited. The publisher and author have the right to use the text, images and other multimedia contents from the submitted work for further usage in affiliated programs. Commercial use and derivative works are not permitted, unless explicitly allowed by the publisher.





