Imaging findings of arterial calcification due to deficiency of CD73: A case study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3941/jrcr.v17i12.5175Abstract
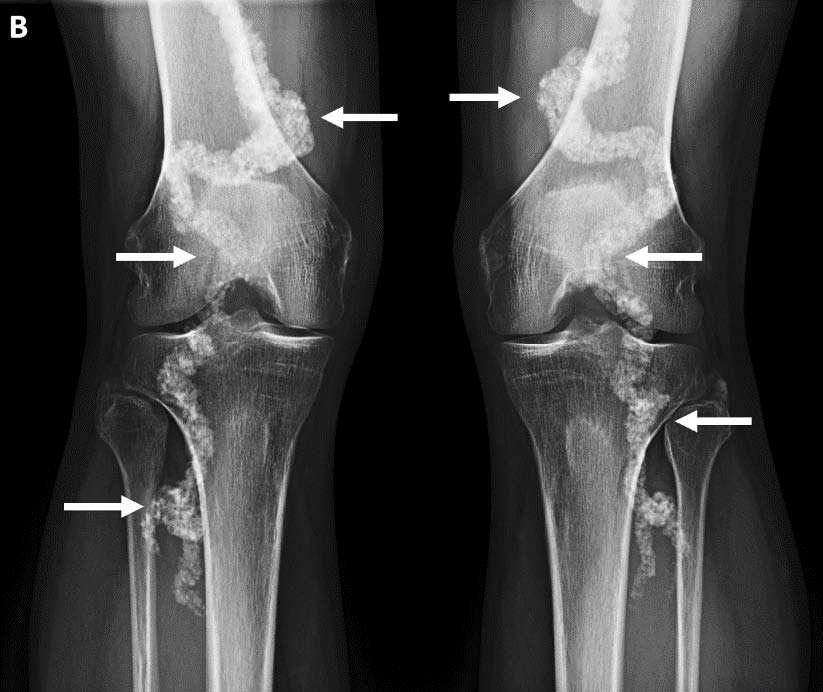
A 52-year-old male developed right knee pain after hiking in Guatemala. On his return he underwent a knee MRI for an indication of medial knee pain, which demonstrated a medial meniscal tear. However, the MRI demonstrated marked tortuosity and dense calcification of the popliteal artery, confirmed on subsequent radiographs. Review of previous CT studies of the abdomen and lower extremities showed severe ectasia and arterial calcification in the femoral and popliteal arteries bilaterally, but no calcifications in the aorta and common iliac arteries. Dual energy CT studies of the extremities demonstrated extensive periarticular soft tissue calcification throughout the wrists, hands, ankle and feet without evidence of uric acid. Review of the electronic medical records revealed a diagnosis of Arterial Calcification due to Deficiency of CD73 (ACDC), a rare genetic disorder presenting with debilitating pain in the wrists and hands, claudication of the calves, thighs and buttocks, progressing to chronic ischemia of the feet which may be limb-threatening. The patient was enrolled in an NIH trial of bisphosphonates and dual-antiplatelet therapy with stabilization of symptoms. This case discusses the imaging findings of this rare condition, differential diagnosis to consider, and current management.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Radiology Case Reports

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The publisher holds the copyright to the published articles and contents. However, the articles in this journal are open-access articles distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 License, which permits reproduction and distribution, provided the original work is properly cited. The publisher and author have the right to use the text, images and other multimedia contents from the submitted work for further usage in affiliated programs. Commercial use and derivative works are not permitted, unless explicitly allowed by the publisher.





